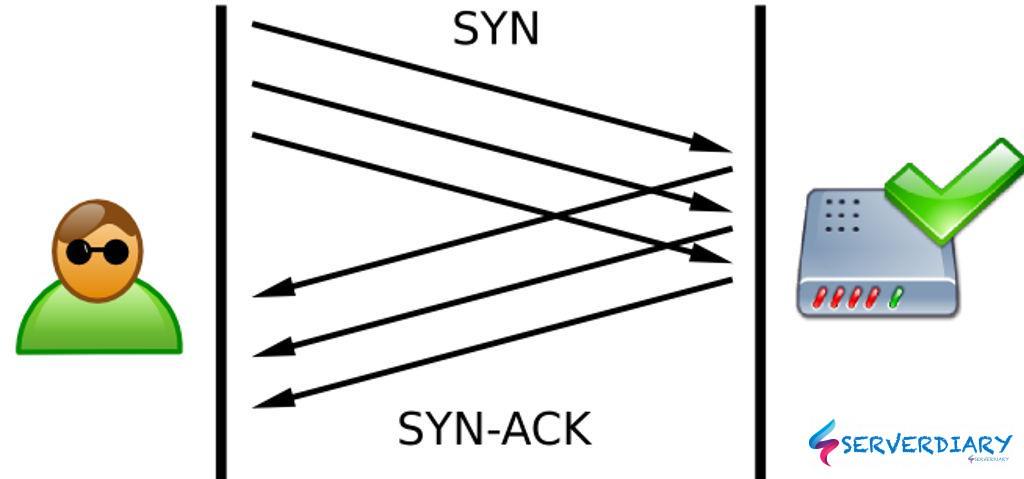
TCP SYN flood is a one type of DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack that exploits part of the normal TCP three-way handshake to consume resources on the targeted server and render it unresponsive.
With SYN flood DDoS, the attacker sends TCP connection requests faster than the targeted machine can process them.
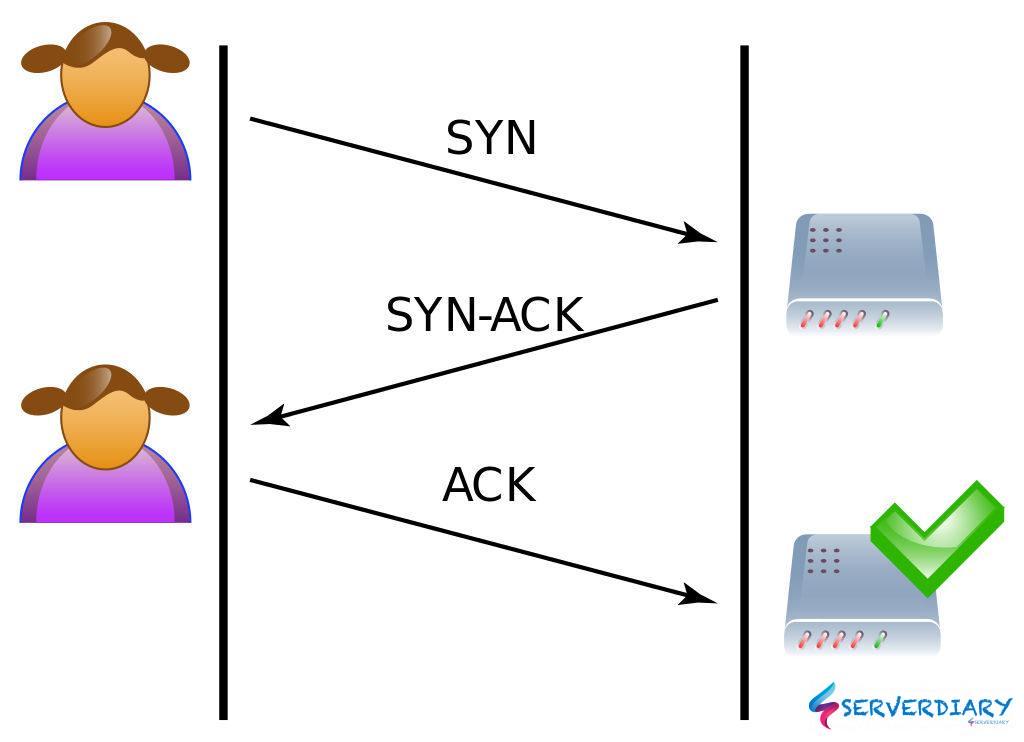
A normal TCP between a client and server establish three-way handshake, the process is looks like this:
- On first connection, client request connection by sending SYN (synchronize) packet to the server
- Then server send responds to that initial packet with a SYN/ACK packet, in order to acknowledge client and server communication
- Client responds with an ACK (acknowledge) message, and the connection is established.
You can read more about TCP SYN Flood on https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/ddos/syn-flood-ddos-attack/
How to mitigate your server is under SYN flood attact:
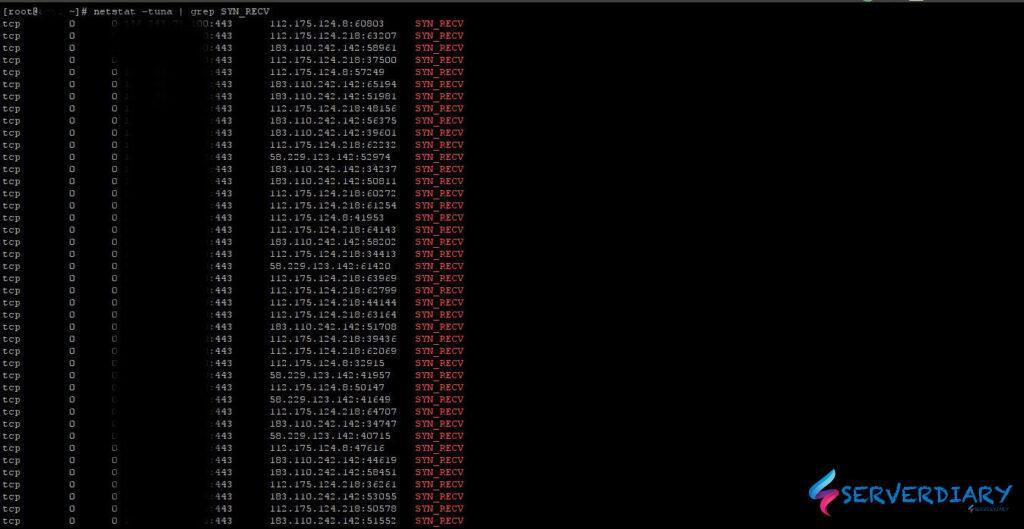
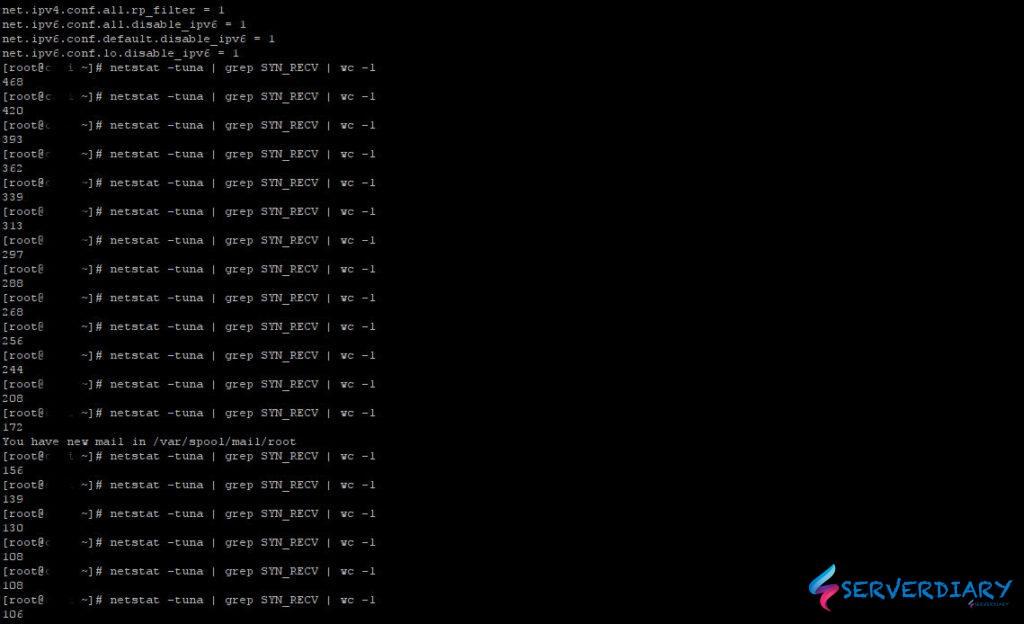
# netstat -tuna | grep SYN_RECVCommand below is counting how much SYN_RECV connection:
# netstat -tuna | grep SYN_RECV | wc -lBelow is sample our server is under “small” SYN flood attact
Many people don’t use optimized kernel settings to better mitigate the effects of DDoS attacks.
We have tried many settings of sysctl.conf , but not one work or not lucky yet until found this settings.
This is CentOS 7 kernel settings that we working.
Edit /etc/sysctl.conf file with code below.
Please note on vm.swappiness=0, we don’t need to use Swap, because our server has 256 GB.
vm.swappiness=0 #This server have 256 GB of RAM, we don't need swap
vm.vfs_cache_pressure=50
vm.dirty_background_ratio = 5
vm.dirty_ratio = 80
vm.max_map_count = 655300
fs.file-max = 2097152
fs.nr_open = 2097152
kernel.printk = 4 4 1 7
kernel.panic = 10
kernel.sysrq = 0
kernel.shmmax = 4294967296
kernel.shmall = 4194304
kernel.core_uses_pid = 1
kernel.msgmnb = 65536
kernel.msgmax = 65536
net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 262144
net.core.rmem_default = 31457280
net.core.rmem_max = 67108864
net.core.wmem_default = 31457280
net.core.wmem_max = 67108864
net.core.somaxconn = 65535
net.core.optmem_max = 25165824
net.ipv4.neigh.default.gc_thresh1 = 4096
net.ipv4.neigh.default.gc_thresh2 = 8192
net.ipv4.neigh.default.gc_thresh3 = 16384
net.ipv4.neigh.default.gc_interval = 5
net.ipv4.neigh.default.gc_stale_time = 120
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max = 10000000
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_loose = 0
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_established = 1800
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_close = 10
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_close_wait = 10
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_fin_wait = 20
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_last_ack = 20
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_syn_recv = 20
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_syn_sent = 20
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_time_wait = 10
net.ipv4.tcp_slow_start_after_idle = 0
net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 1024 65000
net.ipv4.ip_no_pmtu_disc = 1
net.ipv4.route.flush = 1
net.ipv4.route.max_size = 8048576
net.ipv4.icmp_echo_ignore_broadcasts = 1
net.ipv4.icmp_ignore_bogus_error_responses = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_congestion_control = htcp
net.ipv4.tcp_mem = 65536 131072 262144
net.ipv4.udp_mem = 65536 131072 262144
net.ipv4.tcp_rmem = 4096 87380 33554432
net.ipv4.udp_rmem_min = 16384
net.ipv4.tcp_wmem = 4096 87380 33554432
net.ipv4.udp_wmem_min = 16384
net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets = 1440000
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle = 0
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_max_orphans = 400000
net.ipv4.tcp_window_scaling = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_rfc1337 = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_synack_retries = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_syn_retries = 2
net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 16384
net.ipv4.tcp_timestamps = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_sack = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_fack = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_ecn = 2
net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout = 10
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time = 600
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_intvl = 60
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_probes = 10
net.ipv4.tcp_no_metrics_save = 1
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 0
net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_redirects = 0
net.ipv4.conf.all.send_redirects = 0
net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_source_route = 0
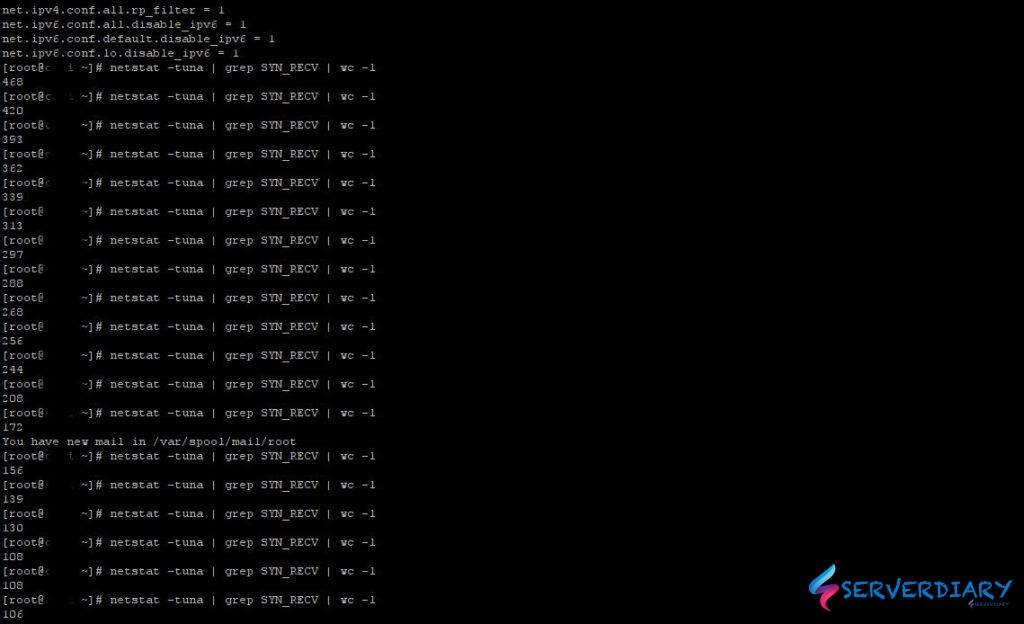
net.ipv4.conf.all.rp_filter = 1To apply setting on /etc/sysctl.conf without restart, use command below.
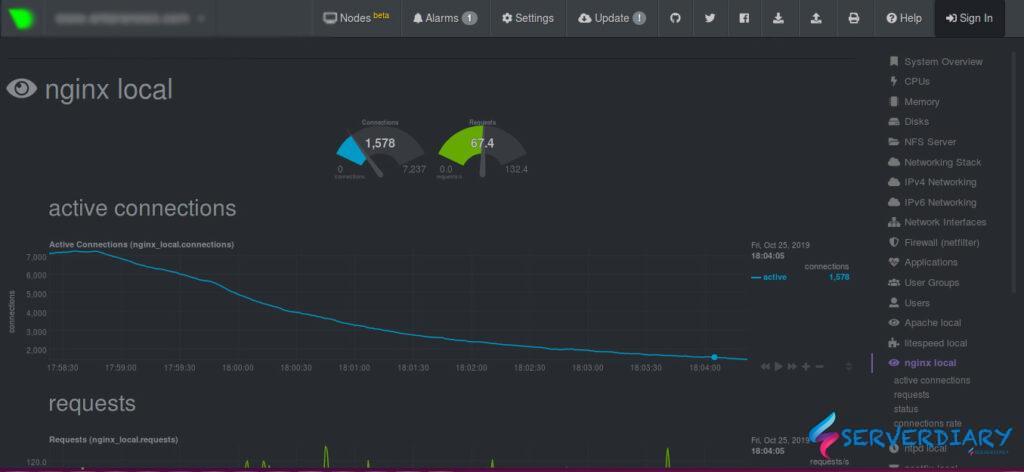
# sysctl -pWhen we under TCP SYN flood attact and we apply /etc/sysctl.conf setting, SYN Flood attact number decrease.
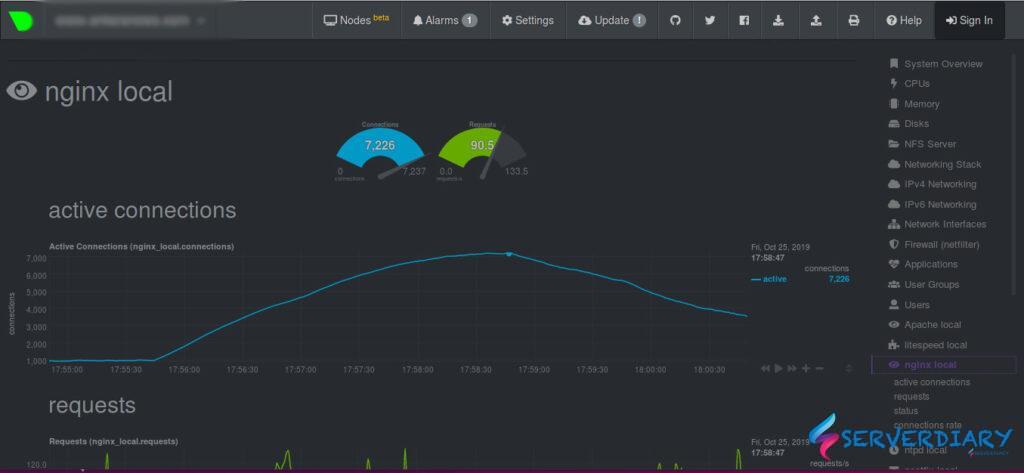
TCP SYN Flood connection will make very high connection on Nginx.
We can check on netdata, about 7.226 active connections on Nginx, with only 90 connection per second.
This condition make slow down Nginx respons.
After we apply sysctl.conf, active connection decrease.